Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, leading to excessive production of thyroid hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. When the thyroid gland becomes overactive, it can wreak havoc on the body, causing a wide range of symptoms and health complications. In this comprehensive blog post, we'll delve into the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, explore its symptoms, and discuss strategies for management and treatment.
Understanding Hyperthyroidism:
The thyroid gland, located in the front of the neck, produces hormones called thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are responsible for regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall body function. In hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland produces an excess of these hormones, leading to a state of hypermetabolism.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism:
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Here are the key steps in diagnosing hyperthyroidism:
Medical History and Physical Examination: The healthcare provider will start by taking a detailed medical history to assess symptoms and risk factors associated with hyperthyroidism. A physical examination may also reveal signs such as a rapid heartbeat, tremors, and enlarged thyroid gland (goiter).
Thyroid Function Tests: Blood tests are essential for evaluating thyroid function. The main thyroid function tests include:
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test: TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the thyroid to produce T4 and T3. In hyperthyroidism, TSH levels are typically low because the pituitary gland senses high levels of thyroid hormones in the blood and reduces TSH production.
Free T4 and T3 Tests: These tests measure the levels of free (unbound) T4 and T3 hormones in the blood. Elevated levels of free T4 and T3 confirm the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism.
Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU) Test: This test involves ingesting a small amount of radioactive iodine and measuring how much is absorbed by the thyroid gland. High uptake of radioactive iodine indicates an overactive thyroid gland.
Thyroid Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the thyroid gland may be performed to assess its size, structure, and any nodules or abnormalities.
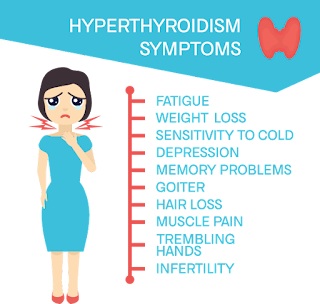
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism:
Hyperthyroidism can cause a wide range of symptoms, which can vary in severity from person to person. Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
Palpitations
Tremors
Weight loss despite increased appetite
Heat intolerance
Excessive sweating
Fatigue
Nervousness or anxiety
Irritability
Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
Frequent bowel movements
Goiter (enlarged thyroid gland)
Thin, brittle hair
Changes in menstrual patterns
Management and Treatment:
The management of hyperthyroidism aims to reduce thyroid hormone levels, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment options for hyperthyroidism include:
Antithyroid Medications: Medications such as methimazole and propylthiouracil (PTU) can block the production of thyroid hormones. These medications are often used as the first-line treatment for hyperthyroidism, particularly in mild to moderate cases.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Radioactive iodine treatment involves taking a radioactive iodine capsule or liquid, which is absorbed by the thyroid gland and destroys the overactive thyroid cells. This treatment is highly effective but may lead to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) in some cases.
Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers such as propranolol or atenolol may be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety.
Surgery (Thyroidectomy): In some cases, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be recommended, particularly if other treatments are not effective or if there's concern about thyroid cancer.
Lifestyle and Self-Care Tips:
In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage hyperthyroidism and improve overall health. These include:
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
Avoiding excessive intake of iodine-rich foods, such as seaweed and iodized salt.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Getting regular exercise to help improve metabolism, reduce stress, and promote overall well-being.
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can worsen thyroid function and increase the risk of complications.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hyperthyroidism is a common thyroid disorder characterized by an overactive thyroid gland and excessive production of thyroid hormones. Diagnosing hyperthyroidism involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including thyroid function tests and radioactive iodine uptake tests. Once diagnosed, hyperthyroidism can be effectively managed with medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition and individual factors. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, individuals with hyperthyroidism can lead healthy, fulfilling lives and minimize the risk of complications associated with the condition. If you suspect you may have hyperthyroidism or are experiencing symptoms suggestive of thyroid dysfunction, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations.
This blog post aims to provide valuable insights into the diagnosis, symptoms, and management of hyperthyroidism, empowering readers to take proactive steps toward better thyroid health and overall well-being. By understanding the signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can effectively manage their condition and optimize their quality of life.
#Hyperthyroidism
#ThyroidHealth
#ThyroidDisorders
#OveractiveThyroid
#ThyroidAwareness
#EndocrineHealth
#ManageHyperthyroidism
#ThyroidTreatment
#ThyroidMedication
#RadioactiveIodine
#ThyroidSurgery
#HealthyThyroid
#ThyroidSupport
#ThyroidSymptoms
#TackleHyperthyroidism
#ThyroidCare
#WellnessWednesday
#HealthTalk
#ThyroidCommunity
#EmpowerThyroidHealth

No comments:
Post a Comment